The company, Ixana, says devices that incorporate its chip will give users the equivalent of a “wearable brain” — sensing and analyzing the person’s environment, and providing real-time information about everything from inventory on a warehouse shelf to a previously forgotten acquaintance at a party.
Ixana raises $3M with breakthrough wearable silicon chip
Ixana, the wearable hardware company developing high-speed human-computer interfaces, today announced it has closed $3 million in seed funding and is backed by Uncorrelated Ventures, Samsung Next, Evonexus, Paradigm Shift and Hack VC.
With new chip, augmented reality startup Ixana claims success in quest for ‘wearable brain’
The three co-founders of Ixana, L-R: Shovan Maity, head of research; Angik Sarkar, CEO; and Shreyas Sen, a Purdue University professor who came up with the new chip.
A previously unknown Seattle startup founded by veterans of the semiconductor and technology industries says it has developed an energy-efficient chip capable of running advanced AI applications on a lightweight, wireless augmented reality headset that can last a whole day without recharging.
Samsung Electronics invests in wearable hardware specialist ‘Drocana’
Samsung Next Participates
in $3 Million Seed Funding Round Drasana Spurs Advancement of Wireless Augmented Reality Headset Technology
All-day Augmented Reality, now possible courtesy of Wi-R
In recent years, the augmented reality (AR) headset space has heated up, with almost every major tech company teasing a headset release soon.
Billions of dollars have been invested in recent years to build AR headsets that are suitable for everyday use, user-friendly, and powerful at the same time. Unfortunately, no company has yet been able to build the all-day productivity companion capable of real-time AI with always-on camera. Technical challenges such as thermal budget and battery drain severely limit capabilities. Reports say overheating is one of the key reasons Apple hasn’t announced their mixed reality headsets yet. Meta CEO, Mark Zuckerberg, calls fitting a computer on the frame of AR glasses “one of the hardest technical challenges of the decade”. Ixana’s Wi-R chip solves this billion dollar problem.
Ixana’s reference AR headset is like a trained second pair of eyes connected to a wearable brain. The front-facing camera can see what you are seeing, analyze it and give you real-time feedback.
Why distributed computing?
Unfortunately, today’s AR headsets are far from being an all-day productivity companion. Thermal budget and battery capacity severely limit usability. AR headset makers have been forced to accept hardware limitations, choosing between a lightweight, all-day wearable form factor, all-day battery life, helpful functionality enabled by real-time machine learning inference or making the headset wire-free. It is challenging to even run real-time inference on the headset camera video all-day, constraining today’s smartglasses to just record and store camera video.
Enabling technology: Wi-R
Ixana aims to challenge those limitations through the development of 100 times more energy efficient silicon chip that is currently being integrated in their Augmented Reality (AR) headsets. Wi-R is a new non-radiative wireless technology with the performance and security of wires, but the convenience of wireless. Compared to Bluetooth, Wi-R offers 100X higher energy efficiency, 10X higher data rates, lower latency, and higher reliability with its interference robustness and low bit error rates. However, Wi-R is confined near the surface which leads to unique advantages in physical security, multi-node co-existence, touch detection, and communication.

How Wi-R enables all-day wearable AR headsets
With the game-changing Wi-R chip, Ixana is developing a reference headset with a total weight under 3oz despite boasting all-day battery life and real time machine learning inference from AR headset camera. Wi-R enables distributed computation using the smarpthone or a different device as the hub. This in turn leads to the posssibility of AR headsets without heavy duty computation that can last all-day on a small battery.
Ixana’s developer kits will be available after CES’23. We are already testing our headsets with enthusiasts and industrial customers. It’s exciting to get this incredible product into the hands of more people.
Looking forward to the world where everyone has a lightweight AR headset that they wear the entire day.
Wi-R enables wearables to harness AI capabilities via distributed computation
We envision a future with distributed wearable computing. Similar to the human body, there would be multiple sensors on body, powered by one distributed computing hub (which we call Wearable Brain). We have coined the term Electronic Nervous System (ENS) for this distributed computing platform. Dr. Shreyas Sen describes the vision in detail in the IEEE Spectrum paper.
What if the brain could leverage the capability of the smartphone processor seamlessly, in real-time, essentially expanding our real-time knowledge to the entire internet? We’d become augmented superhumans.
Why distributed computing?
Our biological brain is amazing when it comes to logical reasoning and dexterity. Machines on the other hand trump the brain when it comes to numerical computation and memory. It’s a pity that even though we have a smartphone in our pocket, the brain can “talk” to the smartphone only when it is held up. What if the brain could leverage the capability of the smartphone processor seamlessly, in real-time, essentially expanding our real-time knowledge to the entire internet? We’d become augmented superhumans. To achieve this high-speed human-computer interaction, the real-time AI processor on the body (Wearable Brain), needs to know what we see, hear and sense. The real-time information capture requires can only be achieved by distributed computing with multiple sensors on different parts of the body. Motion sensors on different parts of the body will enable the Wearable Brain to create a realistic digital twin of our body. No one likes to charge multiple devices every day, so most of these sensors need to be charging-free patches on the body.
Enabling technology: Wi-R
The information processing architecture of the human body is enabled by the incredibly efficient, wire-like nerves. On the other hand, today’s wearables communicate via Bluetooth and other wireless signals which are 10,000 times inefficient compared to nerves. Wi-R is a new non-radiative wireless technology with the performance and security of wires, but the convenience of wireless. Compared to Bluetooth, Wi-R offers 100X higher energy efficiency, 10X higher data rates, lower latency, and higher reliability with its interference robustness and low bit error rates. However, Wi-R is confined near the surface which leads to unique advantages in physical security, multi-node co-existence, touch detection, and communication.

Discourse on the Ixana’s distributed computing vision of the future
Smartphone in our pocket has nearly all of the components required to be an auxiliary brain. However, the challenge is, the smartphone is not communicating with the brain, in real-time. This is the entire reason we use a smartwatch. The smartphone in our pocket can’t help us get a quick peek at the notifications. The pocket is not a good location to capture body physiological signals either. In a way, smartwatch is already abstracting out smartphone functionalities, in a different form factor. And people want that, as is evidenced by the growing smartwatch market. In fact, the number of wearable devices is on the rise with smartwatch, earbuds, various fitness and physiological trackers.
Smartphone basically consists of a screen, processor, memory, bunch of sensors, input ports/protocols and battery. An “out-of-the-box” question to ask, is, do all of these need to be in a single package? What if the sensors, processors and screen were all in different locations on the body?
Why would you do that? Pocket is an undesirable location for a lot of sensors to be. For example, the GPS, could be on your feet. That’s the reason why, smartphone GPS based distance trackers, can’t really track your treadmill run. Heart-rate sensors, pulse monitors etc should be close to the skin. The screen is best placed in an accessible location, e.g. your head or wrists. Battery should ideally be close to the battery-hog electronics e.g. the processor/screen. This is what we call: “deconstructing the smartphone” with distributed computing – placing all of the smartphone components in their most desirable locations on the body. If you believe in the “metaverse” future, sensors on different parts of the body are mandatory to create our digital twin that closely mimics our physical self-all-day.
In Ixana’s distributed computing vision, our body would have a few charging-free electronic patches containing sensors, placed in relevant locations as well as the camera/microphone on the head to register whatever you see/hear. But a centrally placed processor communicates with these sensors unlike today’s wearables, where every wearable has its own CPU.
The major technical bottleneck of distributed wearable computing is communication power. Communication typically consumes 4 orders more power than switching a bit. That’s why every wearable has a CPU to communicate as little as possible. To enable this “deconstructed smartphone” with a single wearable CPU, we need intra-body communication power to at least be 100X lower. Fortunately, Dr Sen has made an important discovery, Wi-R, that makes this possible.
Other technologies that are good to have, to implement this vision of distributed computing include lower power sensors e.g. low power cameras and low power machine learning processors.
Wi-R Technology White Paper
Wi-R is a new non-radiative near-field communication technology that uses Electro-Quasistatic (EQS) Fields for communication. The key differentiations that make Wi-R unique are as follows:
Non-radiative Wire-like wireless
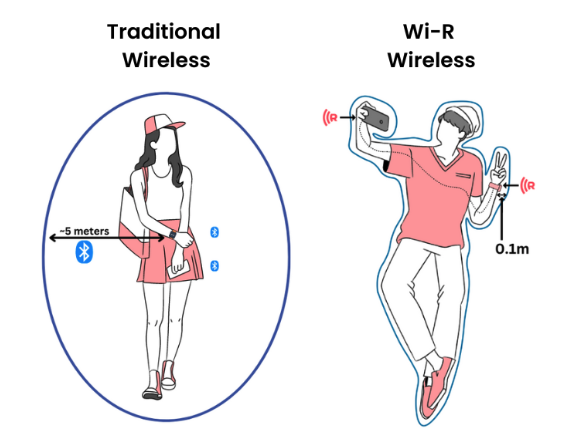
Traditional electromagnetic (EM) field-based wireless (e.g., Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, UltraWideBand (UWB)) radiates signals in every direction. For example, Bluetooth signals can be accessed by anyone in a 5-10m radius. Wi-R, on the other hand, confines the signal around the surface, similar to Wired Communication. Hence, Wire-like Wireless or Wi-R. Someone sitting at your next table doesn’t even have access to the physical signal, leading to energy efficiency and additional physical security on top of the mathematical security that comes from encryption.
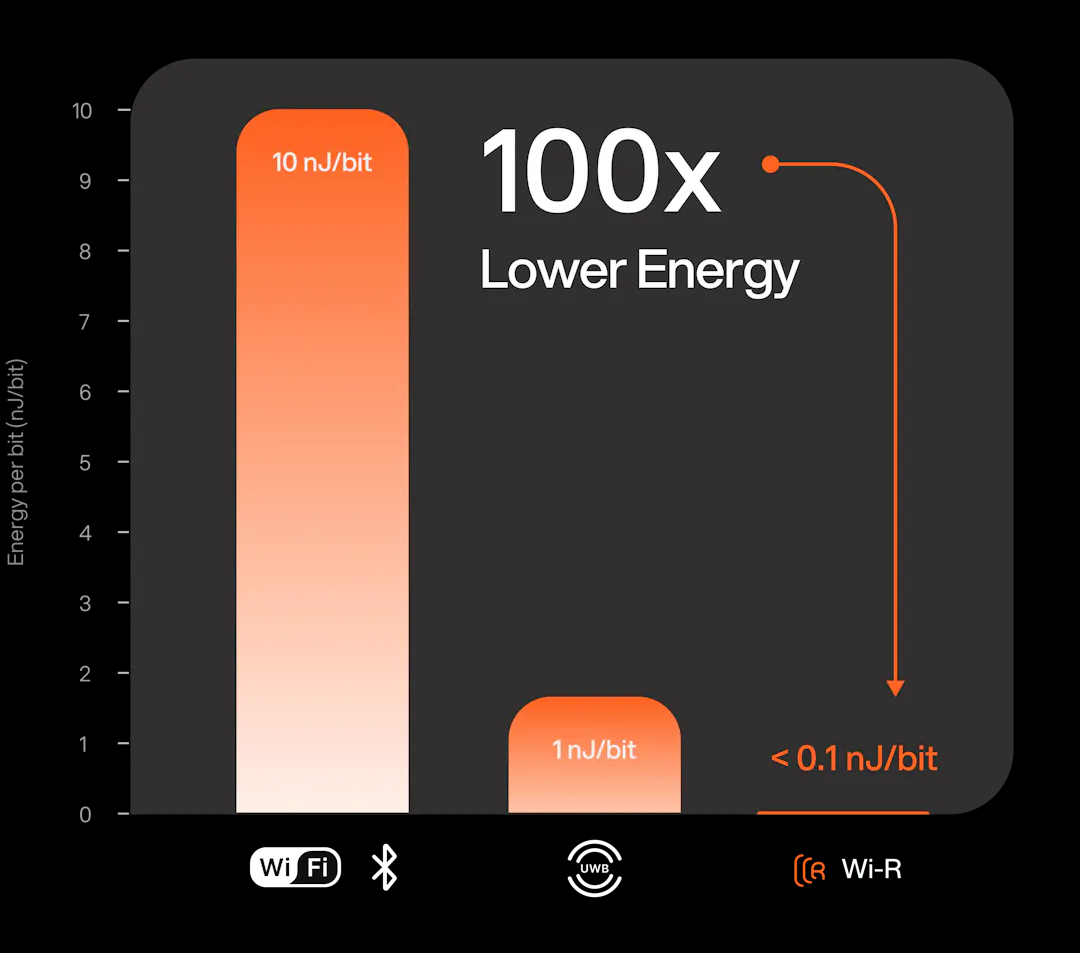
100x more Energy-Efficient than Traditional Wireless
The use of EQS fields, combined with proprietary techniques developed by Ixana, enable communication at 100x lower energy than Wi-Fi or Bluetooth (~10nJ/b) and over 10X lower energy than UWB (>1nJ/b). The inspiration for Wi-R comes from Wired Communication (e.g., USB-C) where ultra-low energy (~1pJ/b) is commonplace. However, the Personal Area Network (PAN) channels utilizing EM waves, such as Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi do not at all look like broadband channels. The key patented invention enabling Wi-R is to develop a broadband channel for the personal area network, enabling wire-like energy efficiencies.
Wi-R is your Personal Secure Broadband solving the “last-meter problem” in Body Area Network (BAN)
For Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), and many other applications of augmented humans, there is a need to connect one or many devices on the human to a central hub on the human. Connecting each device with an off-human router individually is extremely energy-inefficient and reduces channel capacity due to co-existence issues among devices on the same human as well as interactions among devices on multiple humans. Moreover, there is a privacy issue as sensitive data can be snooped from up to 10m away. Wi-R solves these problems by creating an EQS-bubble near the surface (<10cm) which is private, and high-speed. Current prototypes work up to 1Mb/s (good enough for music and images) and up to 20 Mbps prototypes (for video) are under development.
How does Wi-R compare with other Near-field communication techniques?
The prominent near-field communication products available in the market are NFC and NFMI. Near-Field Communication (NFC) is an extremely short-range communication, typically used for payment, etc. Near-Field Magnetic Induction (NFMI) is a longer-range version of NFC and has been commonly used for connecting one earbud to another for relaying audio for synchronous playback in both ears.
Both NFC and NFMI use Magneto-Quasistatic (MQS) Fields, creating a magnetic bubble for communication. They circulate current in an inductor or coil to create magnetic fields that are picked up by another coupled inductor or coil nearby. Humans being transparent to magnetic fields does not provide any particular advantage limiting the range to a few cm for NFC and creates high channel loss for longer distances for NFMI. Moreover, the range is similar between the human as well as away from the human. Finally, to obtain low channel loss often these MQS techniques need to use resonance, which leads to narrowband channels and hence low data rates (~600 Kbps in NFMI) and higher energy (~5 nJ/b).
Conversely, Wi-R can be thought of as the dual of NFMI, which utilizes tiny amount of EQS fields and benefits from moderate conductivity and high permittivity of a structure to confine signal on the conducting structure, i.e., the signals are present throughout the structure but not away from it. This also leads to the ability to create broadband or wideband channels, leading to high data rates (up to 20 Mbps) and extreme energy efficiency (<0.1 nJ/b).
Wi-R tech specs in comparison to other Wireless
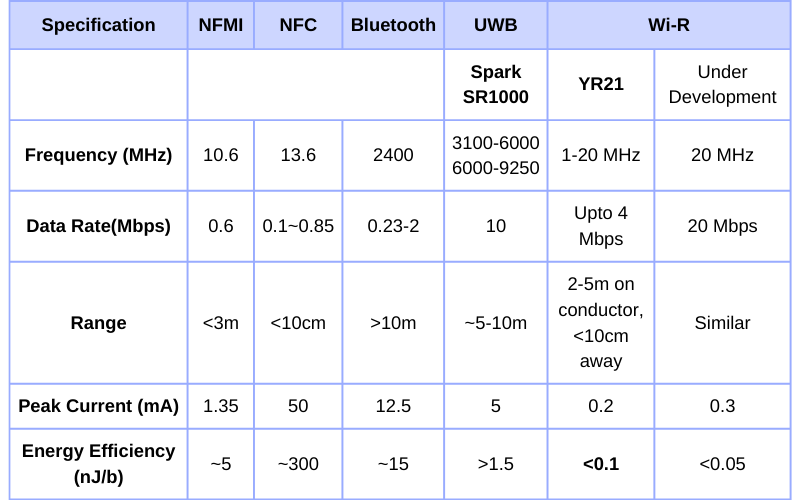
Comparison between different wireless technologies including Wi-R. The numbers for other technologies such as NFMI have been reported from: LINK
What does Wi-R enable that is not possible today?
Wi-R’s transformative capabilities enable applications that are limited by designer imagination (and physics). Some of the prominent features are:
- Combine touch, intent and communication in a single seamless action
- Pairing-free smart devices: No more hassle of pairing. It’s ready as soon as you put it on
- Touch Selectivity: Transfer contacts with a fist bump
- Multiple time-synchronized wearables: Imagine up to 25 body motion trackers
- Ultra-Low-Energy: All-day, real-time, distributed AI
- High-speed: Stream video from AR headset to Smartphone
- Physically secure: Additional layer of Security for sensitive data or action
- Negligible Inter-Human Interference: Increases capacity of communication in a space with multiple humans with each having multiple wearables
- Charging-free Patches: Sensing energy is typically low for many applications. Communication energy and peak power requirements are typically the bottleneck. Wi-R opens the door for long-lasting and even charging-free patches for many low-speed applications by lowering the communication energy by 100x
- Distributed Computing in BAN: Augmenting humans with real-time AI
Why has similar technology not been used before?
While there have been BAN and PAN working groups and much research on Human Body Communication, most, if not all, approaches tried to bring traditional wireless radio techniques to solve this problem, limiting the benefits attainable from these approaches. Especially, using radio-like techniques with EQS fields, the channel loss used to be prohibitively high.
Radios were invented to communicate in a vacuum and over the air. However, they are not the most efficient when trying to conduct over a conducting high permittivity structure such as the human body, suffering from RF signal absorption, and heating in some cases.
Realizing this unique nature of communication required over a conducting structure with high permittivity and given Dr. Shreyas Sen’s unique background in both the Wireless and Wireline IO industry, he and his team brought a fresh take to solving the problem by utilizing EQS fields and creating a wire-like wireless channel that is fundamental to all the achievable benefits.
The first concept came out in 2016 and the first detailed demonstration of the technology happened in 2019. Ixana is the first and only company to bring this transformative technology to market. We believe, Wi-R is a pivotal moment for BAN and PAN.
AR startup Ixana closed a $3 million seed round
AR startup Ixana recently announced that it has closed a $3 million seed round from Uncorrelated Ventures, Samsung Next, Evonexus, Paradigm Shift, and Hack VC.
Ixana’s Wi-R “Wire-Like Wireless” Aims to Put You in Touch With Your Tech’s Comms — Literally
Ixana is hoping to bring about a revolution in communication by, unusually, reducing rather than increasing the range of wireless signals — using a non-radiative “wire-like wireless” system it calls Wi-R and which lets you transfer data, from contact information to streaming video, with a handshake.




